Find out in our article what is meant by Industry 4.0, its benefits and applications.
Let's take a look at the various industrial revolutions in this diagram:
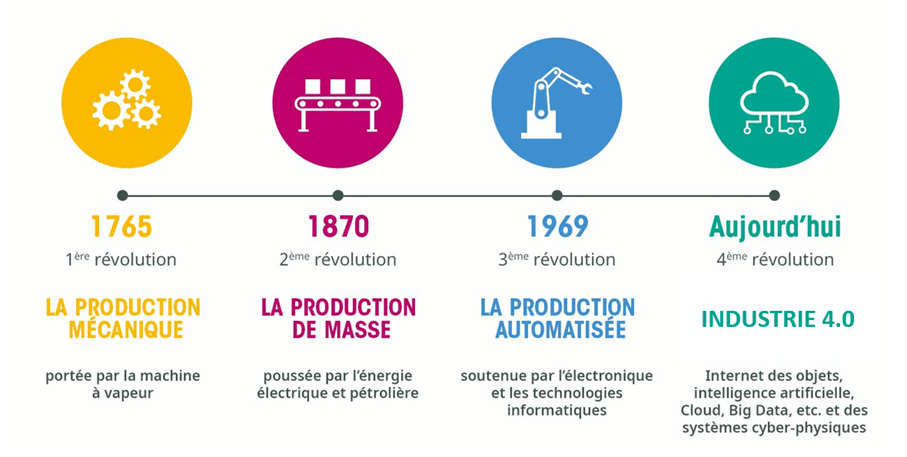
Industry 4.0 (also considered the4th industrial revolution) is therefore linked to the development of new technologies. Production methods are being reorganized around digital technology.
Thanks to these technologies, companies can face up to new challenges. In today's companies, people are at the heart of the business, and employee well-being is becoming a strategic issue. Customer satisfaction is one of the indicators most closely monitored by companies, and the environment is emerging as an unavoidable subject. Performance, meanwhile, continues to be at the heart of corporate concerns.
This revolution is, inevitably, based on these four convictions:
- Improving working conditions for employees
- Improving customer satisfaction
- Reducing environmental impact
- Production optimization
What are the technologies and their application in Plants 4.0?
Many technologies exist to optimize production in Factories 4.0, and they can have many uses.
Here is a non-exhaustive list of these technologies and their applications in plants:
- The autonomous machines Autonomous machines: these technologies capture information about their environment and are capable of modifying their behavior in response to it. A robot can, for example, bring a storage item to the operator by adapting its path to the various obstacles present in the warehouse.

- The cobots cobots: a category of robots designed to manipulate objects in collaboration with humans.

- The virtual reality Virtual reality is a highly immersive way of simulating products, processes and factories.

- The augmented reality Augmented reality is the ability to add a virtual object to the real world. It can be used to accompany technicians in their working environment, for quality control, procedure monitoring, etc.

- The computer-aided design Computer-aided design (CAD): before production, this technique enables a part to evolve virtually in space, and parameters to be modified rapidly.
- The sensors present throughout the warehouse and in all technologies, they enable the retrieval of various types of information.
The information gathered by sensors can be used for many purposes, such as predictive maintenance. In fact, these sensors provide information on the various machines, making it possible to anticipate breakdowns. For example, a variation in pressure, position or noise can be a sign of a future breakdown.
The processing of these vast quantities of data(Big Data) enables relevant information to be extracted rapidly. It can help, for example, to make better forecasts, identify an abnormal situation...
Technologies that stimulate reflection on core business elements
These technologies seem revolutionary for the industry, but their adoption is not so simple.
The " BDC - Industry 4.0: the new industrial revolution " survey of 1,000 Canadian entrepreneurs shows that one in three companies found it difficult to implement these technologies.
Here are the main obstacles encountered:
- Lack of skilled labor
- Excessive costs
- Uncertain return on investment
- Employee resistance to change
- Financing
- Technology complexity
- It's hard to know where to start
- Relevant data analysis
- Cybersecurity
- Data integration
The factory of the future no longer belongs to the distant future, and the benefits promised by new technologies are no longer in doubt. However, setting up such plants is not without its difficulties, which explains the low number of 4.0 plants in operation.
--------
Sources :
- Innovae - Industry 4.0 and augmented and virtual reality
- Webinar "Le numérique, accélérateur de Supply Chain" hosted by Eric David